Geosynthetics for Waste Management
Geosynthetic engineering is the use of synthetic materials in waste and containment projects to achieve more cost effective, safer and more environmentally sound outcomes. The design techniques bring numerous benefits to waste and containment projects, because geosynthetics can better protect the environment, through the control of hazardous leachates and liquors. The fundamental benefits of using geosynthetics in waste management projects are:
- Save costs, firstly by mitigating risk and secondly by reducing high volumes of fill material required, such as sand protection layers and gravel drainage layers
- Remove the risk of variability in traditional lining and drainage systems and gas management - the consistency of product, predictability of performance and ability to provide long term performance data in extreme conditions reduces risk
- Ensuring sound containment protects waterways, fish, animals and the surrounding environment from contaminants. By reducing volumes of fill material required, there is less need to quarry and fewer machines required in construction, reducing the carbon footprint.
- Contain and collect leachate which may be hazardous and well as reducing the production of leachate through capping
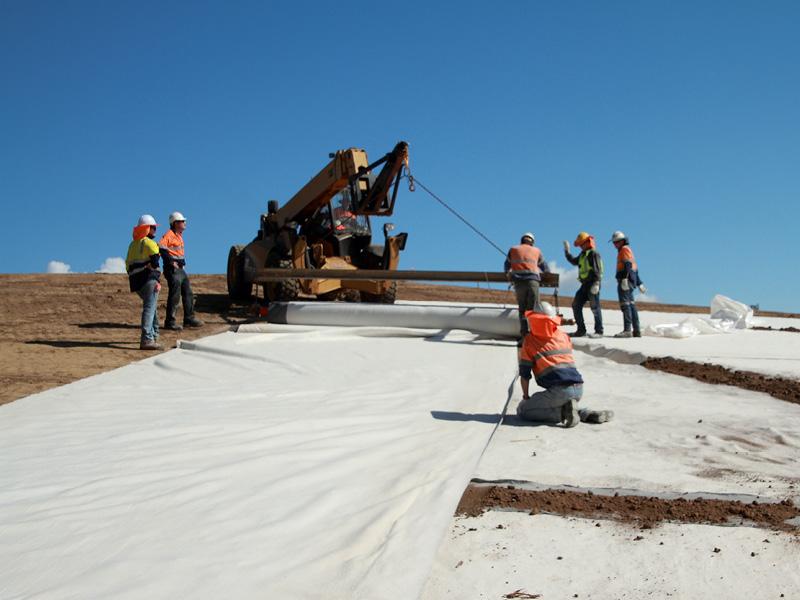


LANDFILL CONSTRUCTION
Geosynthetic engineering allows for the construction of Geosynthetic engineering in landfill where construction can achieve a cost benefit and improved environmental performance when compared to traditional engineering techniques.
APPLICATIONS
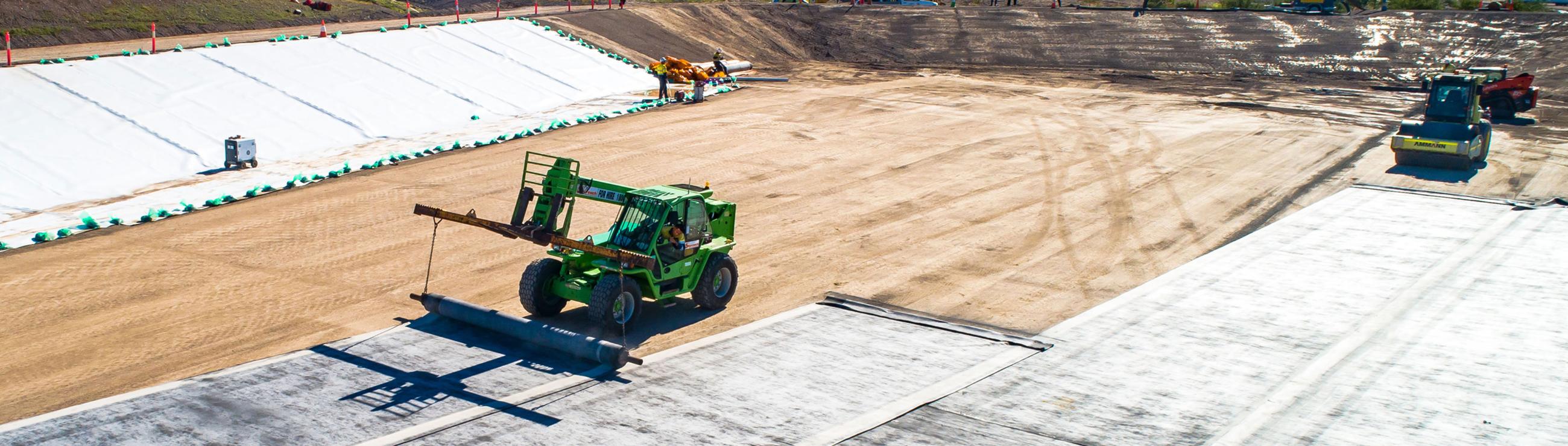
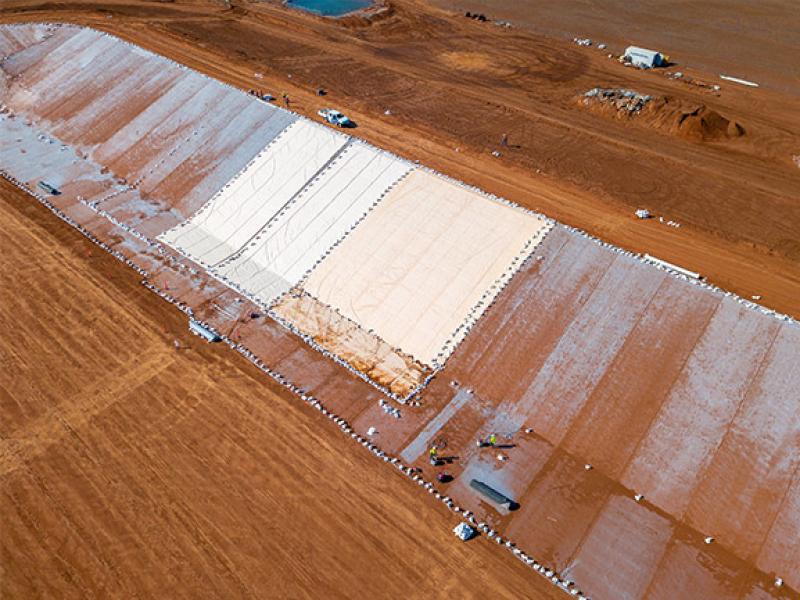
Landfill Lining & Lining Protection
Today’s landfill sites need to withstand increasing waste volumes and more hazardous leachate chemistry. Compacted Clay Liners (CCL), the preferred lining system of the past, now have the potential to react adversely with some leachates resulting in poor performance and the possibility for leachate to contaminate groundwater.
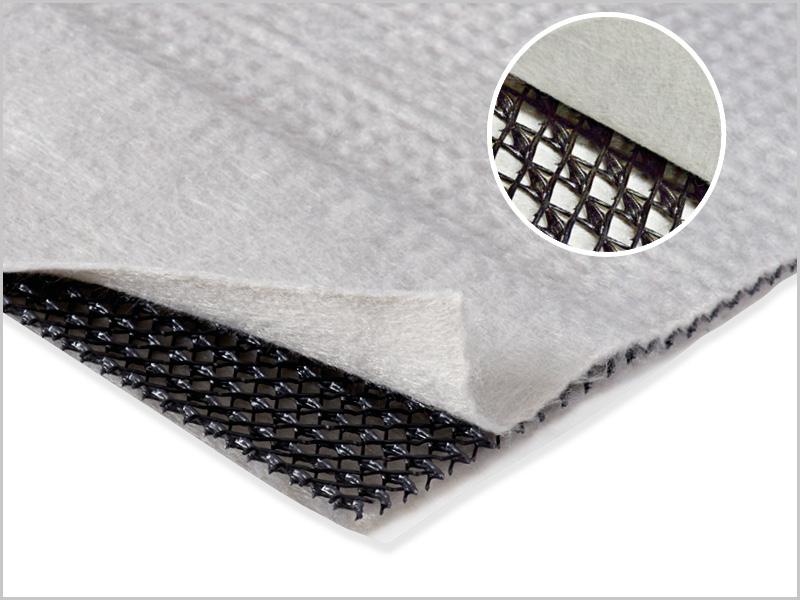
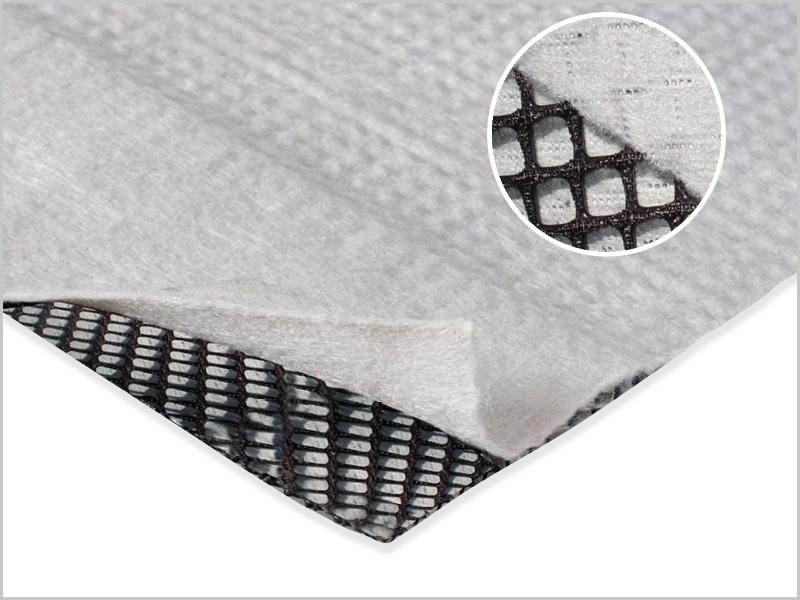
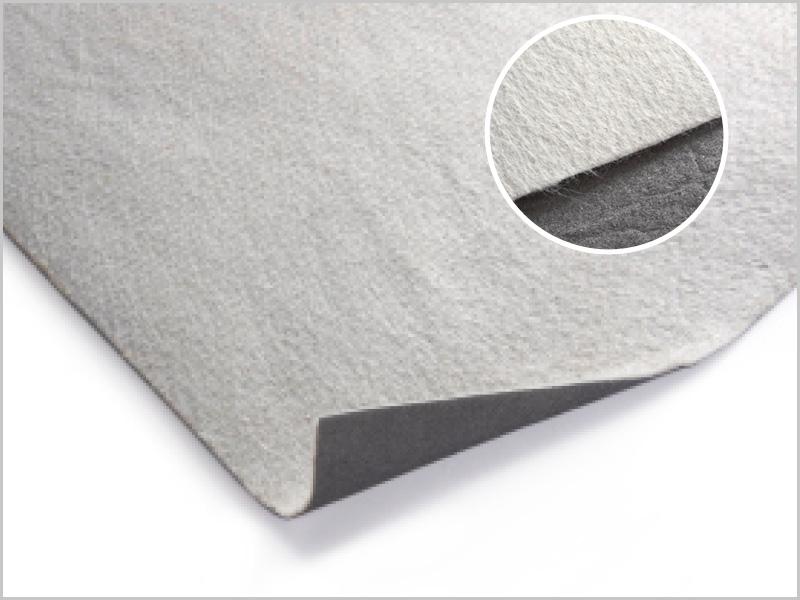
The design aim is to contain and collect leachate through engineered geosynthetic lining systems. A polymeric primary liner (generally HDPE) is now recommended and depending on the leachate chemistry, a secondary liner is used below of either CCL or Geosynthetic clay liner (GCL). We offer comprehensive lining systems comprising our Australian made Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL), Elcoseal and hybrid GCL (hGCL) Sorbseal.
- Lining system at base of landfill cell separates waste from subgrade soils and protects groundwater from contamination of leachates
- GCLs such as Elcoseal can be installed on slopes significantly steeper than the maximum allowable slope for a CCL
- The performance of a GCL must be established with the site chemistry as outlined in the Victorian EPA BPEM Guidelines
- Sorbseal works as a barrier to liquids in the same way as a regular GCL, but also helps trap a wide range of contaminants, including potentially dangerous Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and other emerging contaminants
- Geofabrics has conducted bentonite testing regimes during project supply to establish compatibility and regulatory performance for the life of the project
- Specialty reinforced PVC geomembranes such as Coolguard is engineered for use in areas where primary and/or secondary containment of hydro-carbons, liquids, aggressive chemicals and other regulated substances is required
- Coolpro reinforced polypropylene liners, with exceptional UV resistance excel under some of the most demanding conditions to meet or exceed the critical challenges of liquid containment and pollution control
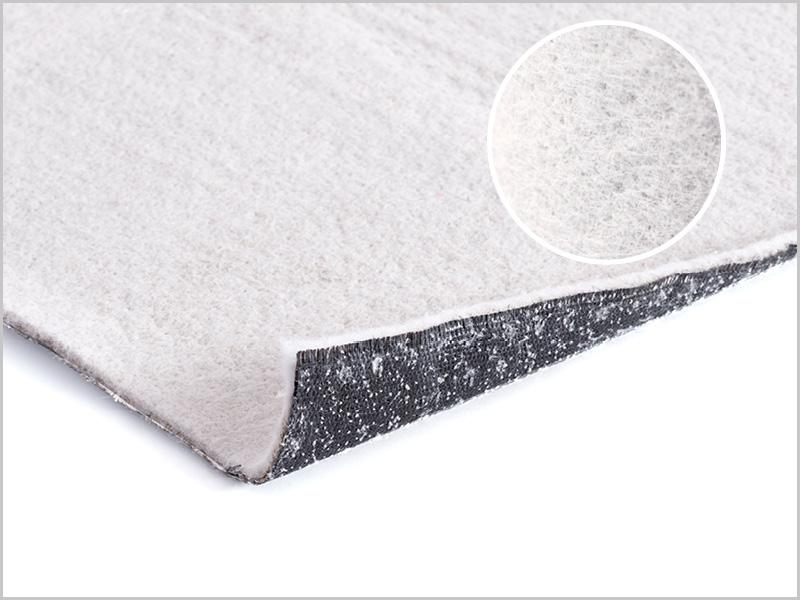
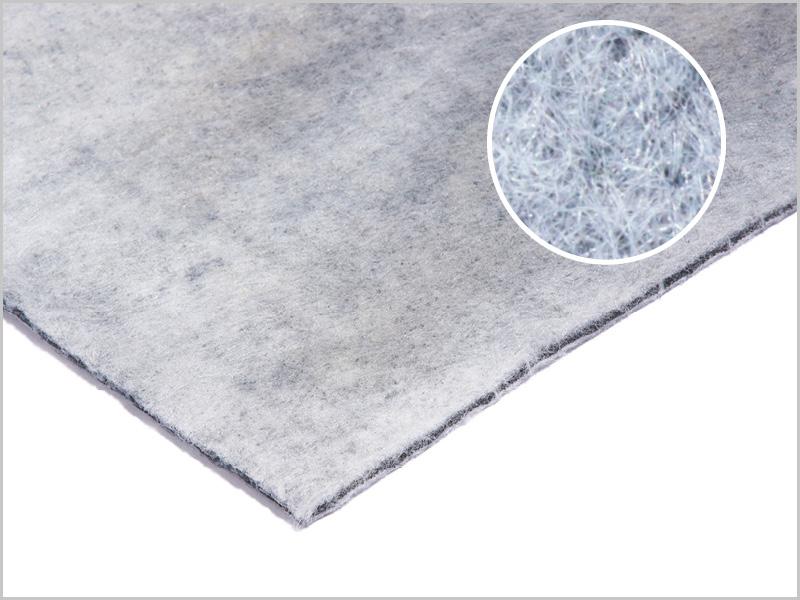
- Cushion geotextiles, including Bidim provide liner protection at a fraction of the cost of a sand protection layer
Leak Detection
The technology built into the Bidim C range of geotextiles offers an effective, lower cost means for designers and installers of lining systems to undertake liner integrity surveys, in newly constructed containment cells.
- Pin holes can be detected in a membrane layer above using standard liner integrity survey equipment
- Installation does not require special skills or equipment as the geotextile does not contain any wires and there is no welding required
- Spark or arc testing can be conducted to ASTM 07953 at as low as 1kV
Gas Collection Systems
Significant quantities of gas are generated from the decomposition of waste in a landfill. The most common gases produced are methane, carbon dioxide and other odorous compounds. It is essential that these gases are vented and captured by an efficient gas collection layer to minimise air pollution.
- If gas collection is not provided, breaches in the capping / closure system can occur
- Flownet biaxial geocomposite can be used in the capping layers to remove gas from below the liner and prevent ‘boils’, or localised areas of high gas pressure
- The gas is able to flow quickly through the two dimensional structure to discharge points where the gasses are diverted
Leachate Drainage Systems
While the Geofabrics team will design a leachate collection system for the potential volumes generated, the primary function is to prevent pressure heads acting directly on the lining system.
- The traditional configuration is a 300mm drainage aggregate covered by a Bidim separation geotextile
- Drainage layers need to be incorporated into base lining systems to lower the hydraulic head on the liner and reduce the heat in the waste body, both of which negatively influence the performance of the system
- With a Trinet triaxial geonet, we can provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional gravel drainage layers on steep side slopes and removes the need for liner protection geotextiles
- Heavy duty geonet provides high flow rates under large confining pressures as the 3-dimensional structure is able to maintain a stable shape which resists crushing
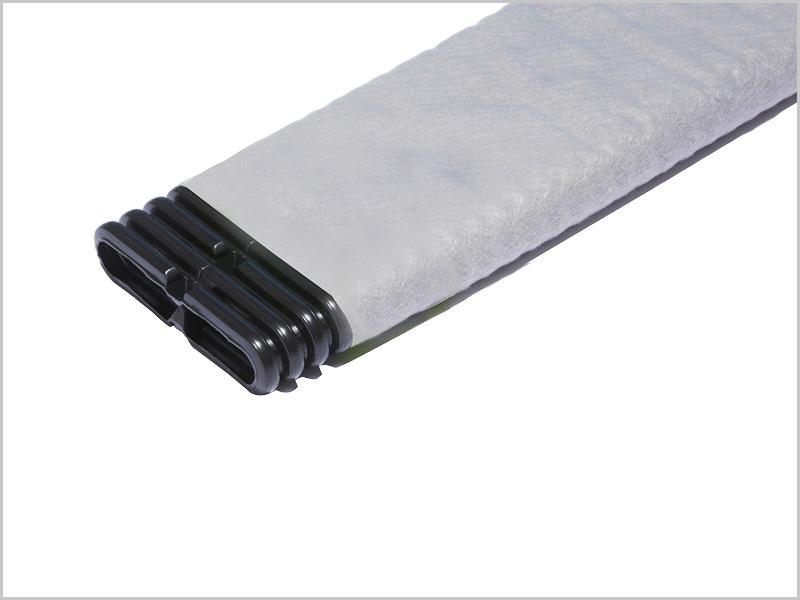
- Megaflo Green flat panel drains provide a simple alternative to trenched round agi pipe drainage systems which are difficult to construct and are often weak points in any lining system
- Megaflo Green is able to resist large vertical loading encountered in many landfill applications, properly designed systems have proven effective under fill depths of up to 70m
Sediment Dams & Leachate Ponds
Removing fine sediments from site runoff can be a costly exercise. Sediment management should include surface erosion products and
silt fences to minimise volumes entering suspension.
- Geotube is a cost-effective dewatering system that uses high strength geotextiles with unique filtration and retention properties
- Dewatering of waste water and sludge is commonly achieved by pumping the slurry into permeable geotextile tubes, treating with site specific flocculants and allowing the moisture to either evaporate through the geotextile or drain through the geotextile pores under significant pressure
- The run-off from the dewatering process can be reused or treated and returned to native waterways while the sediment or waste can be reprocessed or detained
GROUND CONTROL
Geofabrics can assist with effective ground control measures and systems to address slope stability issues and reinforce embankments.
APPLICATIONS
Slope Reinforcement & Subgrade Stabilisation
Geosynthetics can be used to reinforce embankments and steepen slopes constructed from site won material. Tensar RE geogrids and Maccaferri Terramesh systems permit construction of soil slopes up to 70° using a geotextile or mesh face without the need for a full height wall system.
- Maccaferri Terramesh reinforced soil structures provide long term stability, proven longevity, simplicity, cost effectiveness and rapid construction
- Ground stabilisation solutions reduce volumes of imported fill and improve the engineering performance of site soils available for construction
Access Roads
Construction of embankments and platforms over poor quality subgrade material can be costly when importing material. Incorporating
geotextiles or geogrids between poor subgrade and quality fill results in considerable savings in time and materials.
- Approximately 80% more fill is required when constructing over a subgrade of CBR 1 without a geotextile separation (USA Federal Highways Administration)
- Bidim Green non-woven geotextiles are used extensively in construction of roads and embankments over soft ground
- The high elongation characteristics (>50%) of Bidim non-woven geotextiles limits installation damage which ensures long term performance
- Light grade Tensar TriAx can be deployed where subgrade is too soft to allow access for deployment of Bidim Green non-woven geotextiles
Erosion & Sediment Control
Geosynthetic erosion measures can be deployed rapidly to prevent loss of surface sediments and organic deterioration of soils. Long term, the fabric provides a matrix to retain seed and soil and improve the shear resistance of future revegetation.
- The selection of natural and/or synthetic materials depends on the topography, hydraulic conditions and required longevity
- Jute Mesh is an organic, loose weave cargo net mesh used for erosion control and seed establishment used in relatively low flow environments up to 12 months
- In contact with the subgrade, Jute Mesh retains sediment and improves shear properties while restricting overland flow and loss of seed and sediment
- Grassroots is a tight weave synthetic erosion control mat designed to retain maximum sediments while encouraging maximum revegetation
- Able to withstand high velocity water flows both during seeding and sediment control
Hydraulic Engineering & Structures
In waste facilities, Geofabrics can assist in managing variable levels and slopes to ensure an efficient and economical use of the site.
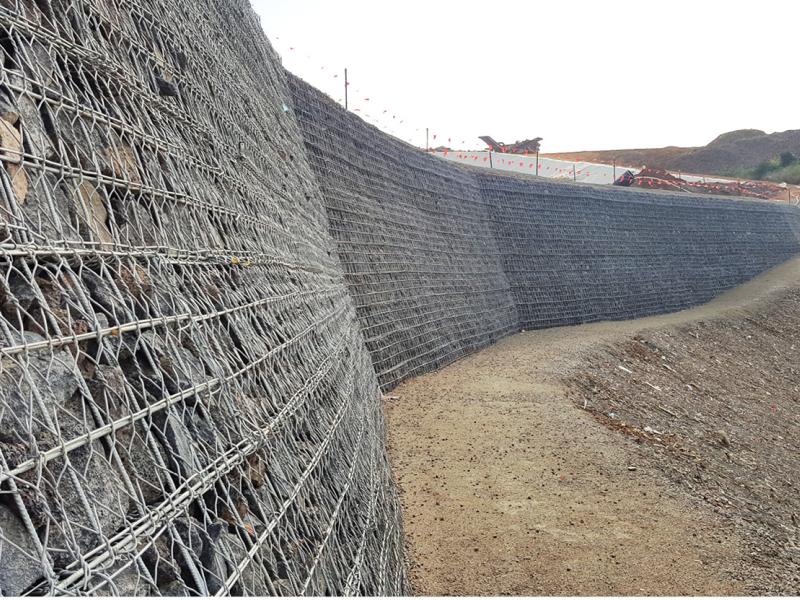
- Gabion wire mesh baskets filled with rock from the site can be used to form flexible, permeable, monolithic structures used for erosion control for bank stabilisation
- Keystone block and Verti-Block systems are fast and economical ways to construct retaining walls where required